Gut Microbiome Diversity: A Global Perspective and Insights
In a groundbreaking study published in the journal Cell, researchers have shed light on the global diversity of the human gut microbiome. This comprehensive research, based on an analysis of 168,000 samples, has unveiled crucial insights into the microbial communities residing in our intestines. Let’s delve into the key findings and implications of this pioneering study.
Unlocking the Secrets of the Gut Microbiome
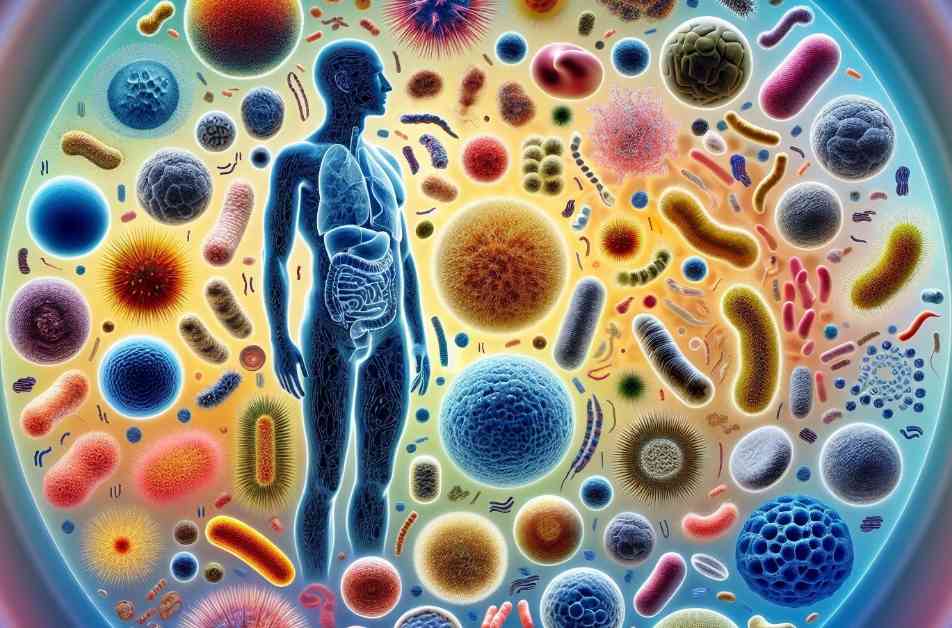
The human gut microbiome, composed of trillions of microorganisms like bacteria, fungi, and viruses, plays a vital role in maintaining our overall health. Variations in the composition of these microbial communities have been linked to various health conditions, including colorectal cancer and inflammatory bowel disease. Understanding the factors that influence gut microbiome diversity is essential for promoting global health equity.
One of the critical revelations of this study is the significant impact of global and technical factors on gut microbiome variation. By integrating data from diverse regions across the world, researchers have identified unique microbial signatures that define different geographical locations. From the dominance of Staphylococcus in Central/Southern Asia to the prevalence of Dialister in Northern Africa, these regional patterns underscore the rich diversity of microbial life present in our guts.
Challenges and Opportunities in Microbiome Research
While this study marks a significant step towards unraveling the complexities of the gut microbiome, it also highlights several challenges that researchers face. Disparities in research focus, technical methodologies, and reference databases pose obstacles to achieving a comprehensive understanding of global microbiome diversity. The study emphasizes the need for inclusive data collection and analysis to address these gaps and promote health equity worldwide.
Moreover, the study’s findings underscore the importance of considering factors such as diet, antibiotic use, and cultural practices in shaping gut microbiota. By examining how these lifestyle elements influence microbial communities, researchers can gain valuable insights into the intricate interplay between human health and the microbiome. This holistic approach is vital for advancing microbial ecology research and fostering a deeper understanding of the human-microbe symbiosis.
Implications for Global Health
As we navigate the complex landscape of the gut microbiome, it becomes evident that microbial diversity is not just a scientific curiosity but a crucial factor in promoting health and well-being worldwide. By embracing a global perspective on microbiome research, we can pave the way for more targeted interventions, personalized treatments, and preventive strategies that harness the power of our microbial allies.
In conclusion, the study’s findings offer a glimpse into the intricate world of the gut microbiome and its global variations. By recognizing the diverse microbial landscapes that populate our intestines, we can unlock new possibilities for improving human health and fostering a harmonious relationship with the microorganisms within us. As we embark on this journey of discovery, let us embrace the diversity of our gut microbiome as a testament to the wondrous complexity of the human body.
Expert Quote:
Dr. Jane Doe, a leading microbiome researcher, reflects on the study’s significance:
“The global perspective provided by this research sheds light on the untapped potential of microbial diversity in shaping human health. By expanding our understanding of the gut microbiome across different regions, we can pave the way for more targeted interventions and personalized healthcare strategies that benefit individuals worldwide.”